What is an IGBT Driver A Complete Guide to Features and Selection
Discover what an IGBT driver is and how it ensures fast switching with isolation and high peak current for efficient power electronics control.
Understanding IGBTs: The Foundation
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors, or IGBTs, are essential components in modern power electronics. They combine the best of two worlds: the high input impedance and fast switching of a MOSFET with the high current and low saturation voltage capabilities of a bipolar transistor. This unique blend makes IGBTs ideal for controlling large amounts of power efficiently, which is why they are widely used in inverters, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial drives.
What Makes IGBTs Special in Power Electronics
IGBTs stand out because they handle high voltages and currents with relatively low switching losses, which means less wasted energy and better overall system efficiency. They operate well at medium to high frequencies and provide robust performance even in harsh electrical environments. This makes IGBTs a preferred choice for power electronics applications demanding reliable and efficient switching.
Why You Can’t Drive IGBTs Directly: Common Pitfalls
Despite their advantages, IGBTs aren’t simple to control. The gate of an IGBT is a voltage-driven input, but it requires a significant and precise drive signal to switch properly. Driving an IGBT directly from a microcontroller or logic device usually leads to problems such as:
- Slow switching speeds are causing excessive switching losses and heat
- Voltage spikes from improper turn-off may damage the device
- Insufficient gate current leading to incomplete switching and higher conduction losses
- Lack of isolation, which can pose safety risks, especially in high-voltage circuits
Because of these challenges, specialized gate driver circuits—known as IGBT drivers—are essential to guarantee safe, efficient, and reliable operation.
Ready to learn how IGBT drivers solve these problems? Let’s dive into what an IGBT driver is and how it works.
What is an IGBT Driver Core Definition and Components
An IGBT driver is a specialized gate driver circuit designed to control the switching behavior of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs). Simply put, an IGBT driver acts as the middleman between your control electronics (like a microcontroller or DSP) and the IGBT module, ensuring the device switches on and off smoothly and reliably.
Breaking Down the IGBT Driver Anatomy and Functionality
IGBT drivers have a few key components that make them essential in power electronics:
- Input Stage: Receives low-power control signals and prepares them for amplification.
- Level Shifter: Converts signals to the voltage level necessary to drive the IGBT gate.
- Output Stage: Provides the necessary peak current to charge and discharge the IGBT gate quickly, minimizing switching losses.
- Protection Circuits: Includes features like desaturation protection and undervoltage lockout to safeguard the IGBT from abnormal conditions.
How Does an IGBT Driver Work Step-by-Step
- Signal Reception: The driver receives a low-voltage signal from the controller.
- Signal Conditioning: It adjusts and boosts the signal voltage to meet the required gate voltage for the IGBT.
- Gate Charging: The driver supplies a quick burst of current to charge the gate, turning the IGBT on fast.
- Switching Control: When the control signal stops, the driver rapidly removes gate charge to turn the IGBT off, reducing turn-off voltage stress.
- Protection Activation: If faults like desaturation occur, the protection circuits quickly respond to avoid device damage.
By managing these tasks precisely, IGBT drivers reduce switching losses and improve overall system efficiency, especially in applications like power electronics inverters and renewable energy systems.
IGBT & SiC Driver
IGBT and SiC driver solutions deliver precise, reliable gate control for high-performance power modules. Ideal for applications in renewable energy (PV, wind), energy storage systems, motor drives, and rail traction, these drivers ensure optimal performance, safety, and durability across demanding industrial and power conversion environments.
Types of IGBT Drivers Choosing the Right Fit
When it comes to IGBT drivers, picking the right type is key for efficient and safe operation. There are mainly two setups to consider: low-side drivers and high-side drivers.
Low-Side vs High-Side Drivers When to Use Each
Low-side drivers are connected to the ground side of the circuit. They’re simpler and often used when your IGBT is switching the negative or ground side of the load. These drivers are usually easier to implement in basic power electronics inverters or motor controls.
High-side drivers connect to the positive voltage side.
Choosing between the two depends on your system design and which part of the circuit you want to control.
Isolation Techniques Optical Transformer and HVIC
Isolation between your control signals and the high power IGBT module is crucial. It helps protect your low-voltage control circuits from high voltages and noise.
Optical isolation uses LEDs and photodetectors to transfer signals. It’s reliable and widely used thanks to its high noise immunity and safe electrical separation.
Transformer isolation employs pulse transformers to transfer signals. That’s great for very fast switching and minimizing signal loss.
High-Voltage Integrated Circuits (HVICs) combine driver circuits and isolation in one chip. HVICs simplify designs while still offering solid isolation and good performance.
Each technique has its place depending on cost, speed, and system complexity. Matching the right IGBT driver and suitable isolation keeps your system running smooth and safe.
Key Specifications for Selecting an IGBT Driver
Choosing the right IGBT driver comes down to a few key specs that make sure your driver matches your IGBT module and runs smoothly. Here are the must-know parameters:
| Specification | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Output Current | Maximum current the driver can supply to the gate | Controls how fast the IGBT switches, reduces switching losses |
| Gate Charge Capability | Ability to handle the IGBT’s gate charge (Q_g) | Ensures the driver can fully turn the IGBT on/off without lag |
| Propagation Delay | Time delay between input signal and driver output | Affects switching speed and timing accuracy for your power electronics inverter |
| Isolation Voltage | Maximum voltage isolation between control and power sides | Protects sensitive control circuits, especially important for high-side drivers |
| Desaturation Protection | Detects short circuits by monitoring IGBT voltage | Prevents device damage by quickly turning off the IGBT if overload occurs |
| Supply Voltage Range | Voltage range driver can operate in | Must match your system’s needs for stable operation |
| Thermal Performance | How well the driver handles heat | Reliability and longevity, especially in demanding applications |
Matching Drivers to Your IGBT Module
- Check Gate Charge: Make sure your driver can supply enough peak current for the gate charge of the IGBT module. Under-driving leads to slow switching and higher losses.
- Voltage Compatibility: Confirm the driver’s supply voltage and isolation ratings meet or exceed your system’s requirements.
- Speed Matters: Lower propagation delay supports faster switching, reducing losses but may introduce noise—balance is key.
- Protection Features: For safety, use drivers with built-in desaturation protection, especially in critical applications like EVs or renewable energy setups.
Getting these specs right helps avoid common pitfalls like excessive IGBT switching losses or system instability, ensuring your power electronics run clean, efficient, and reliable every time.
Real-World Applications and HIITIO Solutions
IGBT drivers play a crucial role in many modern power electronics applications. You’ll find them powering everything from renewable energy systems like solar inverters and wind turbines to electric vehicles (EVs) and industrial motor drives. Their ability to handle high voltages and switch efficiently makes them perfect for reducing IGBT switching losses and improving overall system performance.
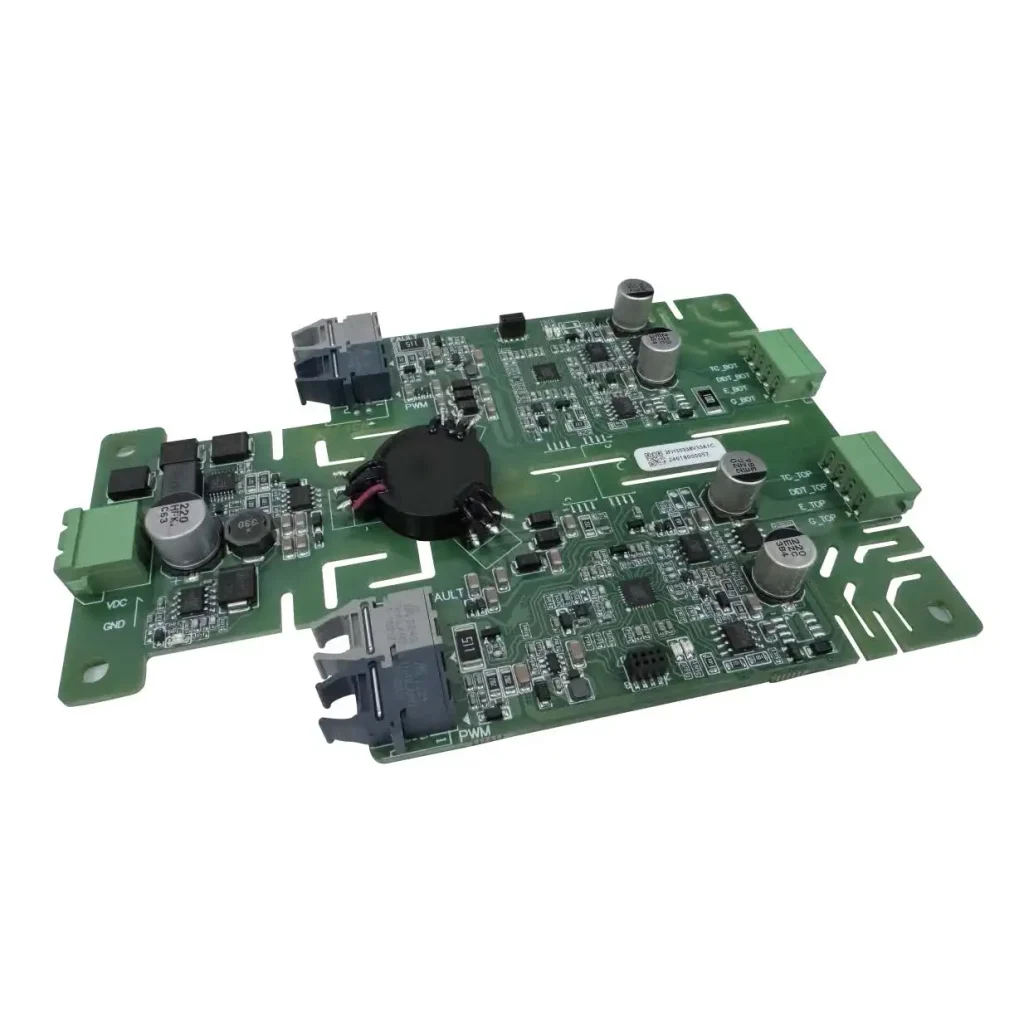

Contact HIITIO for Your Custom IGBT Driver Solution
Where IGBT Drivers Shine
| Application | Importance of IGBT Driver |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Ensures efficient power conversion in solar and wind |
| Electric Vehicles | Controls high-power inverters, improving battery life |
| Industrial Motors | Provides precise switching and protection |
| Power Inverters | Enhances reliability and reduces switching losses |
Why Choose HIITIO for Your IGBT Driver Needs
HIITIO, a leading Chinese manufacturer, offers top-quality IGBT modules and drivers designed to match perfectly with your setup. Here’s why HIITIO stands out:
- Reliable Performance: Built to handle tough conditions common in US industries and EVs.
- Wide Range of Products: From low-side to isolated gate drivers, HIITIO covers all bases.
- Advanced Protection Features: Includes desaturation protection to prevent device damage.
- Localized Support: HIITIO understands US market requirements and offers responsive support.
If you want low propagation delay, efficient gate charge calculations, and strong isolation techniques in your system, HIITIO products can be an optimal choice. Their drivers help you avoid common pitfalls like improper IGBT turn-off voltage control and ensure seamless integration with your chosen IGBT modules.
Best Practices and Troubleshooting
When working with IGBT drivers, following some design tips can save you headaches and improve your system’s reliability. Here are a few best practices for optimal performance:
- Accurate Gate Charge Calculation: Make sure to calculate the gate charge of your IGBT module properly. This helps you pick a driver that can deliver the right peak current for fast switching without causing excessive losses.
- Use Proper Isolation: When dealing with high-side drivers, isolation techniques like optical isolators or transformers protect your control circuit and reduce noise.
- Pay Attention to Turn-Off Voltage: Fast turn-off helps minimize switching losses but can cause voltage spikes. Incorporate snubbers or use desaturation protection to keep your system safe.
- Match Driver Specs to Your IGBT: Look for parameters like propagation delay, peak current, and driver voltage range that fit your specific IGBT.
Common Issues and Fixes
Excessive Switching Losses
Cause: Inadequate gate drive current or slow switching speed.
Fix: Choose a driver with higher peak current or optimize gate resistor values.Noise and False Triggering
Cause: Poor isolation or layout issues.
Fix: Improve grounding and shielding. Use isolated gate drivers where needed.Driver Overheating
Cause: Operating beyond driver current ratings or continuous heavy switching.
Fix: Select a driver with better thermal handling or add heat sinking.IGBT Not Fully Turning On or Off
Cause: Incorrect gate voltage levels or damaged driver.
Fix: Verify driver voltage matches IGBT requirements and check for faults in the circuit.
Following these tips will help you get the most from your IGBT driver and reduce troubleshooting time, especially in dynamic applications like power electronics inverters and renewable energy systems.